lab manual for anatomy and physiology
Summary
Discover the ultimate lab manual for anatomy and physiology. Interactive guides, practical exercises, and real-world applications. Perfect for students and educators seeking hands-on learning.
provides foundational knowledge of the human body‚ emphasizing the integration of structure and function․ This section highlights the importance of laboratory study in understanding anatomical and physiological principles through hands-on experiments and observations․
By exploring key concepts such as cells‚ tissues‚ and body systems‚ students gain a comprehensive understanding of the human body’s organization and its dynamic processes․ This introduction sets the stage for practical applications and real-world relevance in healthcare and scientific fields․
The Key Concepts in Anatomy and Physiology include understanding the levels of organization‚ from cells to systems‚ and the relationships between structure and function․ Students learn essential terms like homeostasis‚ negative feedback‚ and anatomical position․ These concepts form the foundation for analyzing body systems‚ such as the skeletal‚ muscular‚ and nervous systems‚ and their interdependence in maintaining overall health․ Mastery of these principles is crucial for successful lab work and real-world applications in healthcare․
Branches of Anatomy and Physiology encompass various specialized fields‚ including gross anatomy‚ which studies large body structures‚ and histology‚ focusing on microscopic tissue analysis․ Neuroanatomy explores the nervous system‚ while systemic anatomy examines specific systems like skeletal and muscular․ Additionally‚ applied anatomy connects structural knowledge to clinical practices‚ and comparative anatomy investigates differences across species․ These branches collectively provide a comprehensive understanding of the human body‚ essential for healthcare professionals and lab-based learning․
Importance of Laboratory Study in Anatomy and Physiology
The Importance of Laboratory Study in anatomy and physiology lies in its hands-on approach‚ enabling students to visualize and interact with biological structures․ Labs bridge theoretical knowledge with practical application‚ enhancing understanding of complex concepts through dissections‚ microscopy‚ and experiments․ This experiential learning fosters critical thinking and observational skills‚ essential for accurate data collection and analysis․ By engaging in lab activities‚ students develop a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the human body‚ preparing them for careers in healthcare and scientific research․

Structure and Organization of the Lab Manual
The Lab Manual is organized into units‚ each focusing on specific anatomical systems or topics like tissues and histology․ It includes activities‚ exercises‚ and resources for practical learning‚ ensuring a logical flow of content to enhance student understanding and application․
How to Use the Lab Manual Effectively
To maximize learning‚ begin by reviewing the lab manual’s structure and objectives․ Follow step-by-step instructions for each exercise‚ utilizing visual aids like diagrams and charts․ Prepare for lab sessions by reading assigned materials and completing pre-lab questions․ Engage actively during experiments‚ record observations accurately‚ and reflect on outcomes․ Use tear-out worksheets for data collection and review․ Leverage online tools and multimedia resources for additional support․ Regularly review key concepts and seek clarification on complex topics to deepen understanding and retention․
Lab Safety Guidelines and Protocols
Adhere to all safety protocols to ensure a secure lab environment․ Wear personal protective equipment‚ such as gloves and goggles‚ when handling specimens or chemicals․ Familiarize yourself with emergency procedures‚ including the location of fire extinguishers and first aid kits․ Properly disinfect and dispose of biological materials․ Follow instructions for equipment usage and maintain a clean workspace; Report any incidents or hazards immediately․ Always follow your instructor’s guidance and adhere to lab rules to minimize risks and promote a safe learning environment․

Anatomical Terminology and Basic Concepts
Anatomical terminology provides a standardized language for describing body structures and their relationships․ Understanding directional terms‚ body planes‚ and cavities is essential for accurate communication in anatomy and physiology․ These concepts form the foundation for identifying and describing locations‚ movements‚ and functions within the human body‚ enabling precise and clear communication in scientific and clinical contexts․
Understanding Anatomical Directions and Planes
Understanding anatomical directions and planes is crucial for precise communication in anatomy and physiology․ Terms like anterior‚ posterior‚ superior‚ inferior‚ medial‚ lateral‚ proximal‚ and distal describe locations and movements․ The body is divided into three planes: sagittal (vertical)‚ frontal (coronal‚ vertical)‚ and transverse (horizontal)․ These planes help visualize and describe the orientation of structures․ Mastery of these concepts enables accurate description of body organization and is essential for healthcare professionals and students to interpret and communicate anatomical information effectively․
Basic Anatomical Terms and Definitions
Basic anatomical terms provide a standardized language for describing body structures and their relationships․ Terms like proximal (closer to the center) and distal (farther from the center) locate structures relative to a reference point․ Medial refers to the midline‚ while lateral indicates the side․ Dorsal (back) and ventral (belly) describe positions along the body’s axis․ These terms are essential for accurate communication in healthcare and anatomy studies‚ ensuring clarity in describing complex spatial relationships within the human body․
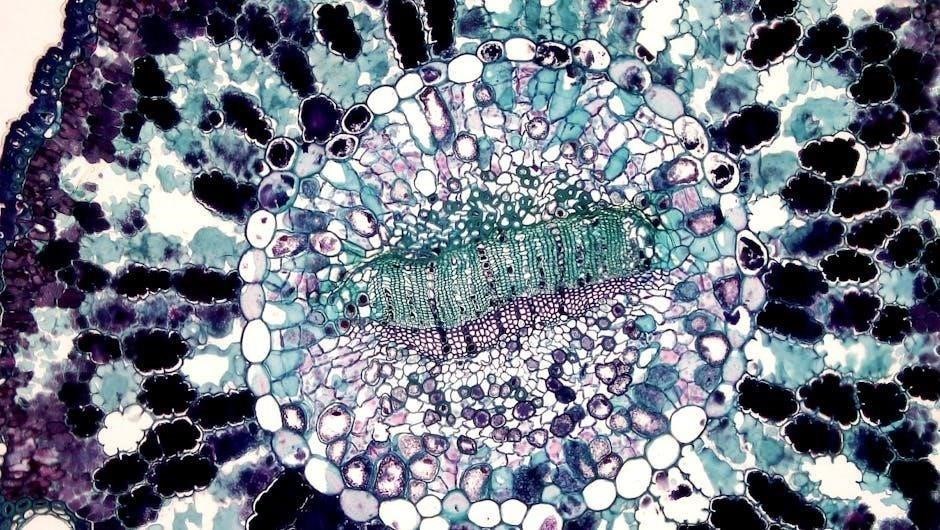
Lab Exercises for Tissues and Histology
Lab exercises introduce students to microscopy and histology‚ focusing on identifying tissue types and their functions․ Practical skills in slide preparation and cellular observation are emphasized․
Microscopy and histology are fundamental techniques in studying tissues and cells․ This section introduces students to the use of microscopes‚ including light and electron microscopes‚ and their applications in observing tissue structures․ Hands-on exercises involve preparing histological slides‚ staining techniques‚ and identifying cellular components․ Virtual microscopy tools are also explored to enhance learning․ These skills are essential for understanding tissue organization and function‚ forming the basis for advanced anatomical and physiological studies․
Identifying Types of Tissues and Their Functions
Four primary tissue types—epithelial‚ connective‚ muscle‚ and nervous—compose the human body․ Epithelial tissues form barriers and line surfaces‚ while connective tissues provide support and structure․ Muscle tissues enable movement through contraction‚ and nervous tissues transmit signals․ Lab exercises involve examining histological slides to identify these tissues‚ understanding their unique characteristics‚ and correlating their structures with functions․ This knowledge is essential for grasping organ system organization and overall bodily functions in anatomy and physiology․
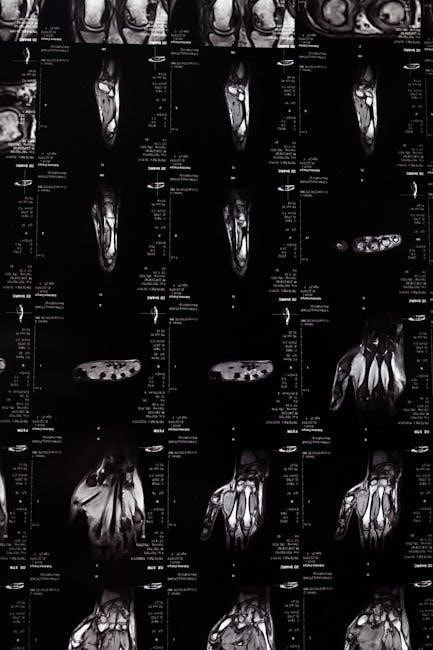
Lab Exercises for the Skeletal System
Lab exercises focus on identifying bone structures‚ such as the axial and appendicular skeleton‚ and understanding their functions in movement and support․ Hands-on activities include bone identification and studying skeletal anatomy to comprehend its role in body structure and movement․
Bone Structure and Identification
Bone structure and identification involve studying the morphology of bones‚ including their surfaces‚ markings‚ and anatomical features․ Students learn to classify bones into categories such as long‚ short‚ flat‚ irregular‚ and sesamoid bones․ Hands-on activities include identifying bones from the axial and appendicular skeleton‚ examining their unique characteristics‚ and understanding their functional roles in movement‚ support‚ and protection․ This exercise enhances observational skills and reinforces the relationship between bone structure and physiological functions․
Axial and Appendicular Skeleton
The axial skeleton consists of 80 bones forming the skull‚ vertebral column‚ ribs‚ and sternum‚ providing structural support and protecting vital organs like the brain and spinal cord․ The appendicular skeleton includes 126 bones in the upper and lower limbs‚ along with the shoulder and pelvic girdles‚ enabling movement and locomotion․ Lab exercises focus on identifying and distinguishing bones from both skeletons‚ understanding their roles in body stability‚ and their anatomical adaptations for mobility and weight-bearing functions․
Lab Exercises for the Muscular System
Lab exercises for the muscular system focus on identifying types of muscles‚ their structure‚ and functions‚ providing practical experience in understanding muscle physiology and their role in movement․
Types of Muscles and Their Functions
The muscular system comprises three types of muscles: skeletal‚ smooth‚ and cardiac․ Skeletal muscles are voluntary‚ attached to bones‚ and enable movement․ Smooth muscles are involuntary‚ found in internal organs‚ and control processes like digestion․ Cardiac muscle is specialized for the heart‚ ensuring rhythmic contractions․ Lab exercises involve identifying these muscles through dissection or microscopy‚ understanding their structural differences‚ and exploring their physiological roles in movement‚ organ function‚ and circulation․
Muscle Structure and Physiology
The muscular system’s structure includes muscle fibers‚ myofibrils‚ and the sarcolemma․ Physiology focuses on contraction mechanisms‚ involving actin and myosin filaments sliding past each other․ Motor neurons stimulate contractions‚ enabling movement․ Lab exercises explore these processes through histological slides and simulations‚ reinforcing the relationship between muscle structure and function in various body movements and physiological responses․
Lab Exercises for the Nervous System
The nervous system lab exercises involve brain dissection‚ neural tissue examination‚ and nerve response analysis to explore neuroanatomy and physiological functions․
Neuroanatomy and Dissection Techniques
Neuroanatomy involves the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system‚ including the brain‚ spinal cord‚ and peripheral nerves․ Dissection techniques allow students to examine neural structures‚ such as cerebral cortex layers and cranial nerves‚ to understand their spatial relationships and functions․ Proper handling of dissecting tools and adherence to safety protocols are emphasized to ensure accurate observations and preservation of specimens for detailed analysis․
Understanding Reflexes and Nerve Responses
Reflexes are automatic‚ involuntary responses to stimuli‚ involving neural pathways that activate effector organs․ Labs explore monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes‚ such as the knee-jerk reflex‚ to demonstrate neural integration․ Students observe how sensory neurons transmit signals to the spinal cord‚ activating motor neurons for rapid responses․ These exercises illustrate the nervous system’s role in maintaining homeostasis and reacting to environmental changes‚ emphasizing the importance of neural communication in human physiology․

Lab Exercises for the Integumentary and Sensory Systems
Labs explore the structure and function of the skin‚ including histological examinations of epidermal layers․ Sensory receptor identification and response testing provide insights into sensory perception mechanisms․
Structure and Function of the Skin
The skin‚ the body’s largest organ‚ consists of the epidermis‚ dermis‚ and subcutaneous layers․ The epidermis‚ outermost‚ protects against pathogens and UV radiation‚ while the dermis contains blood vessels‚ nerves‚ and glands․ Subcutaneous tissue insulates and cushions․ Labs involve histological examinations to identify skin layers and appendages like hair follicles and sweat glands․ Activities focus on understanding the skin’s protective‚ regulatory‚ and sensory functions‚ emphasizing its role in maintaining homeostasis and overall physiological balance․
Exploring Sensory Receptors and Special Senses
Laboratory exercises focus on identifying sensory receptors and understanding their roles in detecting stimuli․ Students analyze the structure and function of special senses‚ such as vision‚ hearing‚ taste‚ and smell․ Activities include testing sensory thresholds and observing histological preparations of sensory organs․ These hands-on experiences enhance comprehension of how sensory pathways transmit information to the nervous system‚ enabling perception and response to environmental changes․

Lab Exercises for the Respiratory and Digestive Systems
Lab exercises for the respiratory and digestive systems involve dissection of organs like lungs and stomachs to study their structures and functions․ These activities help students understand the roles of these systems in processes such as respiration and digestion․
Dissection of Respiratory Organs
The dissection of respiratory organs provides hands-on experience in identifying structures like the lungs‚ trachea‚ and bronchi․ Students examine the internal anatomy of these organs‚ exploring their functional roles in respiration․ Histology slides of respiratory tissues are also analyzed to understand cellular structures․ This exercise enhances understanding of how oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide is expelled‚ linking anatomical features to physiological processes․ It prepares students for clinical applications by familiarizing them with the respiratory system’s intricate design and function․
Understanding Digestive System Anatomy
The study of the digestive system anatomy focuses on the structures responsible for breaking down food into nutrients․ Through dissection and observation‚ students explore key organs such as the mouth‚ esophagus‚ stomach‚ small intestine‚ and liver․ Lab exercises emphasize identifying external and internal features‚ like the stomach’s rugae or intestinal villi․ This hands-on approach helps students link anatomical structures to their physiological roles in digestion‚ absorption‚ and waste elimination‚ providing a clear understanding of how the digestive system functions as a whole․

Lab Resources and References
This section provides essential resources‚ including recommended textbooks like Marieb and Hoehn’s Anatomy & Physiology‚ online tools‚ and citation guides for proper referencing in lab reports․
Recommended Textbooks and Online Tools
For a comprehensive learning experience‚ key textbooks like Marieb and Hoehn’s Anatomy & Physiology and online tools such as PhysioEx™ and Mastering A&P™ are highly recommended․ These resources provide interactive simulations‚ virtual dissections‚ and practice exercises to enhance understanding․ Additionally‚ online platforms like Lumen Learning offer open-source lab manuals and multimedia content․ Many lab manuals also include access to digital tools‚ ensuring a blended learning approach․ These resources support both classroom and laboratory-based education effectively․
Citing Sources and Avoiding Plagiarism in Lab Reports
Proper citation is essential in lab reports to maintain academic integrity and avoid plagiarism․ Always credit sources using styles like APA‚ MLA‚ or CSE․ Paraphrase information and use direct quotes sparingly․ Tools like citation generators can help format references accurately․ Plagiarism undermines credibility and can lead to serious consequences․ Ensure originality by properly attributing all external ideas‚ data‚ and images․ This practice upholds ethical standards and promotes transparency in scientific writing․