physical therapy leg strengthening exercises pdf
Summary
Boost leg strength with expert physical therapy exercises. Download free PDF guide now!

Physical therapy leg strengthening exercises are essential for improving mobility, balance, and overall lower limb function․ These exercises, often detailed in PDF guides, focus on targeting key muscle groups to enhance strength and stability, aiding in recovery and preventing future injuries․
Importance of Leg Strengthening in Physical Therapy
Leg strengthening is a cornerstone of physical therapy, enhancing mobility, balance, and overall lower limb function․ Strong legs improve stability, reduce injury risk, and support daily activities like walking and climbing stairs․ Strengthening exercises target key muscle groups, promoting proper alignment and joint stability․ This is especially vital for recovery after injuries or surgeries, as it restores lost strength and flexibility․ Additionally, leg strengthening helps prevent future issues, such as knee or hip problems, by ensuring proper biomechanics․ A well-designed program, often outlined in PDF guides, tailors exercises to individual needs, fostering long-term independence and improved quality of life․ Consistency in these exercises yields significant benefits․
Overview of the Role of PDF Guides in Exercise Programs
PDF guides play a crucial role in physical therapy exercise programs by providing clear, structured instructions for leg strengthening exercises․ These guides typically include detailed descriptions, step-by-step instructions, and visual aids to ensure proper form and technique․ They are often tailored to individual needs, outlining specific exercises, repetitions, and frequencies․ PDFs are accessible and easy to follow, making them ideal for home-based programs․ Many guides also emphasize safety, offering tips on progression and pain management․ By standardizing exercise routines, PDF guides help patients stay consistent and informed, fostering adherence and effective recovery․ They serve as a valuable resource for both patients and therapists to track progress and achieve therapy goals․

Key Components of a Leg Strengthening Program
A comprehensive leg strengthening program includes targeted exercises, proper warm-ups, and the use of equipment like resistance bands․ Consistency and progression are vital for optimal results․
Warm-Up and Stretching Routines
A proper warm-up and stretching routine are crucial to prepare the muscles for leg strengthening exercises․ Begin with light cardio, such as marching in place, to increase blood flow․ Dynamic stretches like leg swings and high knees can improve flexibility․ After strengthening exercises, perform static stretches, such as seated hamstring stretches or standing hip flexor stretches, to reduce muscle tension․ Always hold stretches for 20-30 seconds and avoid bouncing․ This routine helps prevent injury, enhances range of motion, and supports overall muscle recovery․ Consistency in these practices ensures a safe and effective exercise program․ Proper technique is essential for maximum benefit․
Essential Equipment: Resistance Bands and Ankle Weights
Resistance bands and ankle weights are versatile tools for leg strengthening exercises․ Resistance bands provide adjustable tension, making them ideal for exercises like leg raises, hip abductions, and knee extensions․ They are lightweight, portable, and cost-effective․ Ankle weights add resistance to movements such as straight leg raises and hip flexion, targeting specific muscle groups․ Both tools allow for progressive overload, enabling you to increase intensity as strength improves․ Proper use ensures safety and effectiveness․ Always attach bands to sturdy objects and start with lighter weights to avoid strain․ These equipment options are perfect for home or clinical settings, offering a convenient way to enhance leg strength and stability․
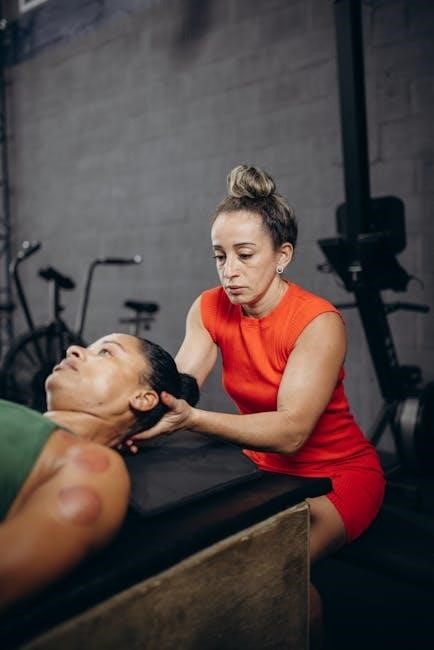

Types of Leg Strengthening Exercises
Leg strengthening exercises are categorized into non-weight-bearing, weight-bearing, and advanced movements․ These exercises target different muscle groups, improving strength, stability, and functional mobility effectively․
Non-Weight-Bearing Exercises: Heel Slides and Straight Leg Raises
Non-weight-bearing exercises are ideal for individuals recovering from injuries or surgeries, as they minimize stress on the legs․ Heel slides involve lying on your back and sliding one heel toward your body, holding for a few seconds before returning․ This movement strengthens the hamstrings and improves knee mobility․ Straight leg raises are performed by tightening the thigh muscles and lifting the leg without bending the knee, enhancing quadriceps strength․ Both exercises are gentle on the joints and can be done in bed or on the floor, making them accessible for early-stage rehabilitation․ Consistency is key for optimal results․
Weight-Bearing Exercises: Squats and Step-Ups
Weight-bearing exercises, such as squats and step-ups, are fundamental for building leg strength and improving functional mobility․ Squats involve bending the knees while maintaining an upright posture, working the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes․ Step-ups target the quadriceps and promote balance by stepping onto a sturdy platform․ Both exercises enhance joint stability and are often used in physical therapy to restore mobility after injuries or surgeries․ Proper form is crucial to avoid strain, with emphasis on keeping the chest up and knees aligned with toes․ Starting with body weight and gradually adding resistance, such as ankle weights, can increase intensity․ These exercises are versatile and effective for progressing leg strength in a controlled manner․
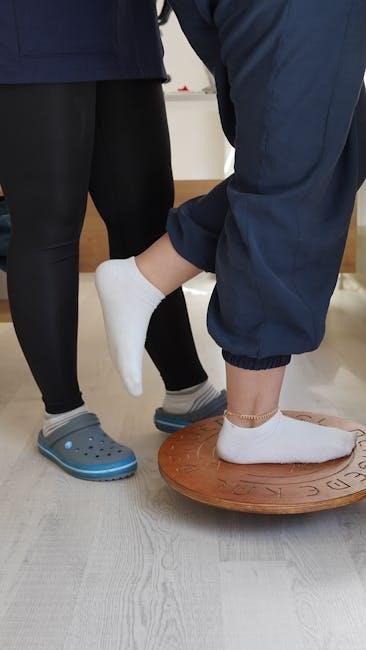
Advanced Exercises: Lunges and Balance Training
Advanced exercises like lunges and balance training are designed to challenge coordination, strength, and stability․ Lunges involve stepping forward and lowering the body, engaging the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes․ They improve functional mobility and balance․ Balance training incorporates single-leg stands, heel-to-toe walks, and wobble board exercises to enhance proprioception and core stability․ These exercises are typically introduced after mastering basic strengthening movements․ Proper form and focus are essential to prevent injury․ Lunges can be modified by reducing depth or using support, while balance exercises often progress by increasing difficulty, such as closing eyes or using unstable surfaces․ These advanced techniques prepare individuals for dynamic, real-world activities․
Progressing Your Exercise Routine
Progressing your routine involves gradually increasing resistance, repetitions, or duration as strength improves․ Transitioning from seated to standing exercises enhances balance and functional strength over time․
Increasing Resistance and Repetitions
To progress effectively, gradually increase resistance using ankle weights or bands and boost repetitions as strength improves․ Start with 1-2 sets of 10-15 reps, aiming to reach 3 sets of 20 reps․ This gradual progression ensures muscles adapt without overexertion․ Always maintain proper form to prevent injury and maximize benefits․ Consulting your physical therapist for guidance on appropriate increases is recommended․
Transitioning from Seated to Standing Exercises
Transitioning from seated to standing exercises is a crucial step in advancing your leg strengthening program․ Seated exercises provide a foundation for building strength and control, but standing exercises enhance balance and functional strength․ Begin by mastering seated movements, ensuring proper form and muscle activation․ Once comfort and strength are achieved, gradually incorporate standing exercises like squats or step-ups․ This progression mimics real-life activities, improving coordination and stability․ Always prioritize proper posture and engage core muscles to support your movements․ TransitioningToo quickly can risk injury, so consult your physical therapist to ensure readiness․ This step is vital for achieving long-term leg strength and mobility․
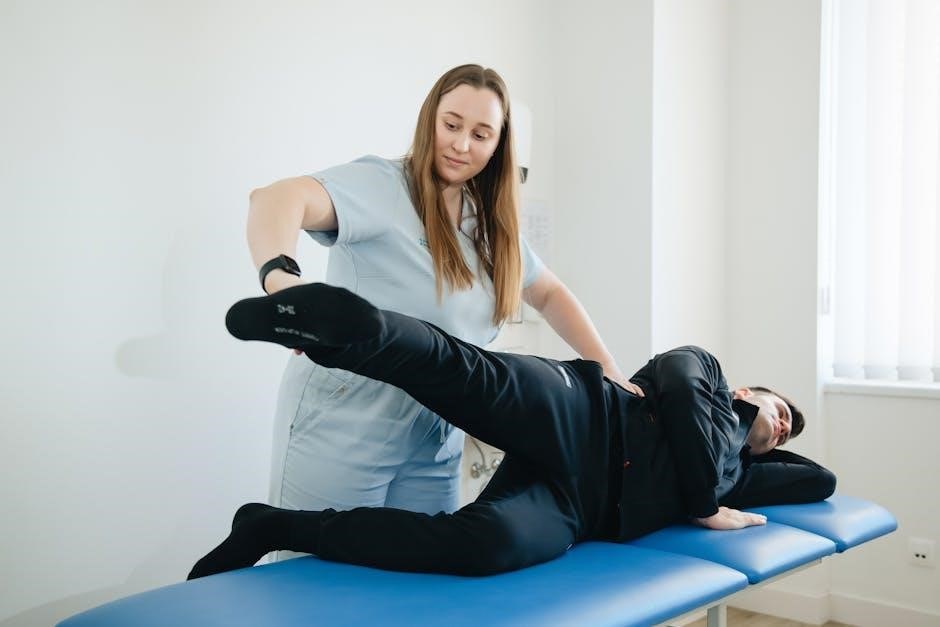
Safety and Precautions
Always prioritize pain-free movement and stop exercises if discomfort arises․ Avoid holding your breath, as it can increase blood pressure․ Perform movements smoothly and controlled, ensuring proper posture to prevent injury․
Understanding Pain and When to Stop
Pain is a signal to stop and assess your exercise technique or intensity․ If discomfort persists, consult your physical therapist to modify the routine․ Avoid pushing through pain, as it may worsen injuries or delay recovery․ Proper breathing techniques, such as exhaling during effort, help maintain stability and prevent strain․ If you experience sharp pain, numbness, or tingling, cease the exercise immediately and seek professional guidance․ Adjustments, like reducing resistance or range of motion, can help you continue safely․ Prioritizing pain-free movement ensures effective and sustainable progress in your leg strengthening program․ Always listen to your body to avoid setbacks․
Proper Breathing Techniques During Exercises
Proper breathing is crucial for maintaining stability and preventing strain during leg strengthening exercises․ Exhale slowly during the exertion phase of each movement to help stabilize your core and maintain proper form․ Avoid holding your breath, as it can increase blood pressure and cause dizziness․ Inhale before starting the exercise, then exhale as you perform the active phase, such as lifting your leg or bending your knee․ This rhythmic breathing helps ensure a steady flow of oxygen to your muscles, enhancing endurance and reducing fatigue․ Consistent breathing patterns also improve focus and technique, making your exercises more effective and safer․
Monitoring Progress and Seeking Professional Help
Regularly track strength and flexibility improvements․ Consult your physical therapist if pain occurs or progress plateaus․ Adjust exercises as needed for optimal recovery and to avoid injury․
Tracking Improvement in Strength and Flexibility
Monitoring progress in leg strengthening exercises is crucial for ensuring effectiveness․ Start by noting the number of repetitions and resistance levels used initially․ Gradually increase these as strength improves․ Flexibility can be assessed by measuring range of motion before and after exercises․ Use a journal to document daily achievements, helping identify patterns and plateaus․ Celebrate small milestones to stay motivated․ If progress stalls, consult your physical therapist for adjustments․ Regular assessments ensure exercises remain challenging yet safe, promoting consistent improvement in both strength and flexibility over time․ This structured approach supports long-term recovery and muscle development․
When to Consult Your Physical Therapist
It’s important to consult your physical therapist if you experience persistent pain or discomfort during exercises․ Additionally, seek guidance if you notice limited progress in strength or flexibility despite consistent effort․ Your therapist can reassess your program and make necessary adjustments․ If you’ve had recent surgery or an injury, they can tailor exercises to your specific recovery needs․ Furthermore, consult them if you feel unsure about proper form or resistance levels․ Regular check-ins ensure your program remains safe and effective, helping you achieve your goals without setbacks․ Open communication with your therapist is key to a successful rehabilitation journey․
Consistency and patience are key to achieving lasting leg strength through physical therapy exercises․ Incorporate these routines into your daily life for sustained improvement and overall well-being․
Consistency and Patience in Your Exercise Routine
Consistency and patience are crucial for effective physical therapy leg strengthening․ Regular performance of prescribed exercises ensures gradual muscle development and joint stability․ Avoid rushing progress, as overexertion may lead to setbacks․ Focus on proper form and technique to maximize benefits․ Celebrate small achievements to stay motivated․ Over time, consistent effort will yield noticeable improvements in strength and mobility, supporting long-term recovery and overall well-being․ Remember, patience is key to achieving lasting results and preventing future injuries․ Stay committed to your routine for optimal outcomes․
A healthy lifestyle beyond physical therapy is vital for sustaining leg strength and overall well-being․ Incorporate balanced nutrition, regular cardio, and adequate rest to support muscle recovery․ Stay hydrated to maintain joint health and prevent stiffness․ Engage in low-impact activities like swimming or cycling to promote longevity of leg strength․ Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol, as they hinder muscle recovery․ Managing stress through mindfulness or meditation can also enhance physical progress․ By adopting these habits, you create a holistic approach to health, ensuring the benefits of physical therapy endure long after treatment ends․ Consistency in lifestyle choices complements exercise routines for lasting results․Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle Beyond Therapy